
Sucrose is divided into white sugar, brown sugar, soft white sugar, rock sugar and raw sugar. The molecular formula is C12H22O11, and its alias is β-D-fructofuranosyl-ah α-D-glucopyranoside, English Sucrose. It is formed by dehydration of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose. It is easily soluble in water but difficult to dissolve in ethanol. Its sweetness is second only to fructose. It is an important food and sweet condiment.
In recent years, with the rapid development of high-performance liquid chromatography, this method has become a widely used detection method in the current analysis of carbohydrates. It has the advantages of high resolution, good repeatability, and high accuracy. Check out the micro-source detection laboratory Literature data used high-performance liquid chromatography to detect rice seeds.
Using Chuangjie HPLC-MS for detection. Accurately weigh 0.03g of sucrose standard and place it in a volumetric flask, add an appropriate amount of ultrapure water, and dissolve it with ultrasound to adjust the volume. Then take a 25mL volumetric flask, weigh 5.0mL of the standard stock solution, add ultrapure water, and dilute to the mark to create a mixed standard solution. All standard solutions are stored in the refrigerator and removed and returned to room temperature before use. The soluble sugar solution of fresh rice seeds was used as the sample to be tested.
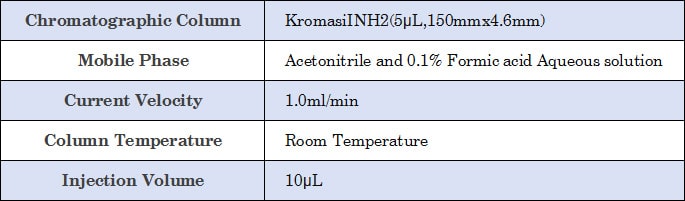
The mass spectrometry conditions used electrospray ionization negative ion collection mode; capillary voltage: 3.2kV; cone voltage of 20 V, extraction voltage: 4.0V to measure sucrose, radio frequency voltage: 0.5V, source temperature: 120°C, desolvation temperature: 300℃, desolvation gas: 300L/h, cone backflush gas: 10L/h. The retention time of sucrose is 7.89 min respectively.
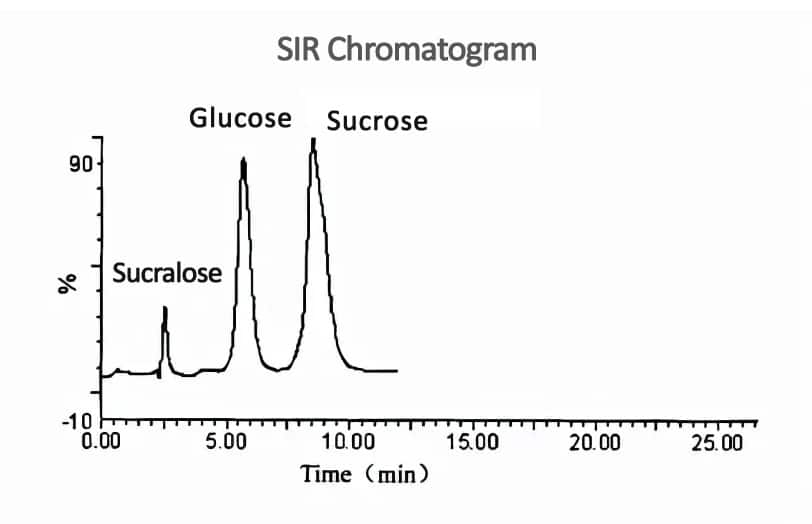
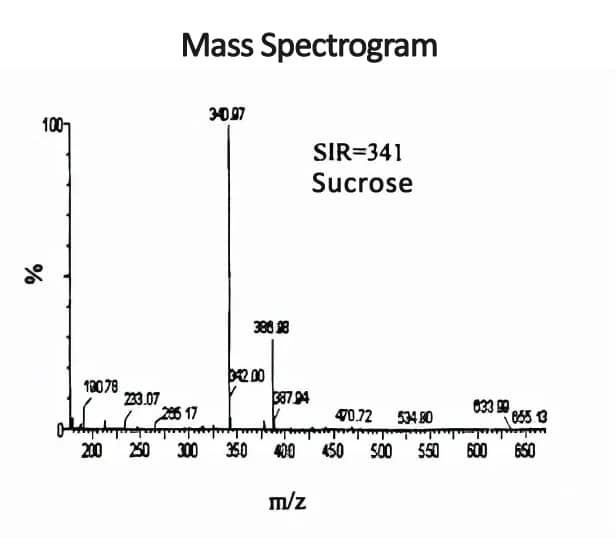
The HPLC-MS method is used to detect sucrose components, which is fast, simple to operate, and accurate. The sensitivity of the determination is also greatly improved, providing a method reference for accurately detecting the sugar content in medicines and foods.
